
- ATOM DEFINITION CHEMISTRY FOR WINDOWS 10
- ATOM DEFINITION CHEMISTRY PC
ATOM DEFINITION CHEMISTRY FOR WINDOWS 10
Adobe photoshop express for windows 10 is a free photo editing software, which allows users to enhance, crop, share, and print. Photo editor is a very handy allows you to crop, rotate and flip the image. This all in one photo editing app for windows 10 lets you create double exposure photos, use stickers or add text to your photos. Now reopen the photo or video in the Photos app to see if you can save the. Across 'Attributes', uncheck the Read-only box. Steps to Remove Read-Only From Photos/ Videos: Right-click on the file you are not able to save and select Properties. Using your keyboard, press the Windows Key + i to open Settings. If it doesn't, please make sure your Windows is also up to date. Check the Photo's app after rebooting and see if it now works properly for you. After the updates complete, close the Store and then reboot your computer. Main Description of DripArt: Photo Editor App: DripArt is the best, free photo editor comes up with the cool dripping effect, camera, collage maker and the editing tools to face tune selfies.
ATOM DEFINITION CHEMISTRY PC
The DripArt: Photo Editor App For PC Windows 10, 8, 7, XP or even on Mac Desktop and Laptops computers.
Here you can get another best Premium app for you. 6 You can now close the File Explorer windows if you like. 4 Paste (Ctrl+V) the selected files from the backup in step 3 into the Settings folder from step 2. 1 If the Photos app is currently open, close it. Restoring a backup of your settings in the Photos app will replace the current app settings. The zinc anode also acts as the battery’s container in zinc-carbon batteries so as it oxidizes during use, the contents can start to leak over time.To Restore Settings to Photos app. In single use, dry cell batteries, zinc is commonly used as the anode whilst manganese dioxide is a popular choice for the electrolyte cathode. As this ionic substance reacts with the electrodes it generates electrical current. In between the electrodes is an electrolyte liquid or gel that contains charged particles – ions. Batteries have two electrodes made of conductive material, the cathode which is the positive end where the electrical current leaves/electrons enter, and the anode where the electrical current enters/ electrons leave. Ionic properties are central to the function of batteries too. Ion-exchange chromatography for example relies on the affinity of the molecules being separated for the stationary phase based on their charge properties to enable separation. Ionic properties can be exploited by chemists for a range of purposes. One example is hydrogen, which may gain (H -) or lose (H +) an electron, forming hydride compounds such as ZnH 2 (where it is an anion) and hydron compounds such as H 2O (where it is a cation).Įlements in group 18 of the periodic table – the “noble gases”, tend not to form ions due to the arrangement of their electrons which makes them generally unreactive. However, some elements are capable of forming both cations and anions given the right conditions. iron, silver, nickel), whilst most other nonmetals typically form anions (e.g. Halogens always form anions, alkali metals and alkaline earth metals always form cations. It can be possible to predict whether an atom will form a cation or an anion based on its position on the periodic table. Examples include calcium chloride (CaCl 2), potassium iodide (KI) and magnesium oxide (MgO). These oppositely charged ions then attract one other to form ionic bonds and produce ionic compounds with no overall net charge. Therefore, when atoms from a metallic and a nonmetallic element combine, the nonmetallic atoms tend to draw one or more electrons away from the metallic atoms to form ions. Conversely, most nonmetallic atoms attract electrons more strongly than metallic atoms, and so gain electrons to form anions. Consequently, they tend to lose electrons and form cations. Metallic atoms hold some of their electrons relatively loosely. 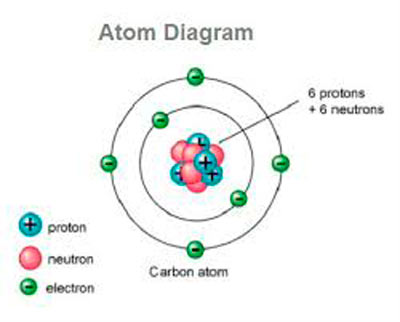
/GettyImages-168181143-7f7b66d27b444016b820db85bf9b7fa0.jpg)
Sodium (Na +), Iron (Fe 2+), Ammonium (NH 4 +)Ĭhloride (Cl -), Bromide (Br -), Sulfate (SO 4 2-)

The main differences between cations and anions are summarized in the table below.



/GettyImages-168181143-7f7b66d27b444016b820db85bf9b7fa0.jpg)



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
